Frequency converter technology plays a transformative role in various industries by enabling the efficient and optimized operation of electrical equipment. It is a critical component in many sectors that rely on precise control of motor speed and torque, energy efficiency, and optimized performance. In this expanded article, we explore some of the industries that reap the most significant benefits from this technology, delve deeper into its specific applications, and highlight the advantages it brings to these sectors.
By providing detailed insights into the use cases, technical advantages, and long-term benefits of frequency converters, this guide will help readers understand why this technology is an essential part of modern industrial and commercial operations.
What is a Frequency Converter?
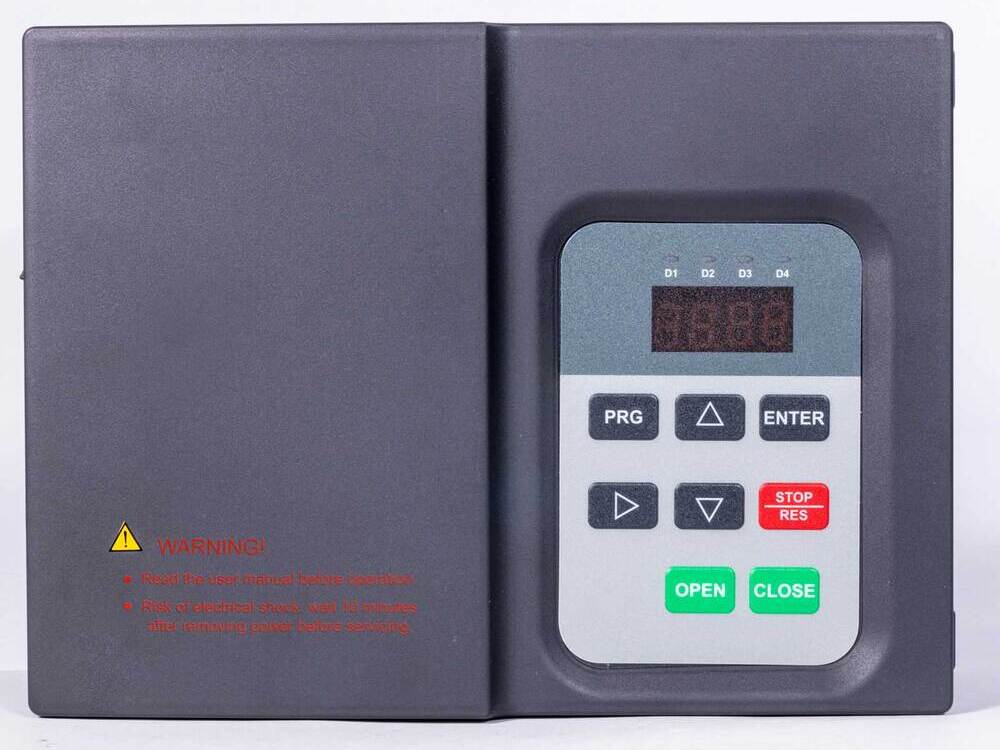
A frequency converter, also known as a variable frequency drive (VFD) or inverter, is an electronic device that converts the frequency of an electrical supply to regulate the speed and torque of alternating current (AC) motors. By controlling motor performance, frequency converters offer numerous benefits, including energy savings, improved process control, and reduced mechanical stress on equipment.

Key Industries and Applications of Frequency Converter Technology
1. Manufacturing Industry
The manufacturing industry is heavily reliant on the precise control of motors for various processes, making frequency converters indispensable. These converters enhance productivity, reduce energy consumption, and minimize waste.
Industrial Automation
Frequency converters are at the heart of industrial automation, providing control over AC motors used in various manufacturing processes:
Production and Assembly Lines: Frequency converters allow for the fine-tuning of motor speed and torque, enabling the adjustment of production processes based on material type, product complexity, and production needs. This results in increased throughput and reduced material waste, essential for industries where efficiency is critical, such as automotive manufacturing, electronics, and consumer goods production.
Material Handling Systems: In modern manufacturing facilities, automated material handling systems like conveyors, robots, and automated guided vehicles (AGVs) rely on frequency converters for smooth operation and precise positioning. By controlling the speed and torque of these systems, frequency converters help enhance safety, reduce energy consumption, and prevent mechanical wear and tear.
Metal Processing
In metal processing industries, where precision is paramount, frequency converters are used to control motor-driven machinery:
Rolling Mills: Frequency converters are crucial for maintaining consistent speed and torque in rolling mills. This ensures uniform thickness and quality of metal sheets and strips, which is vital for industries such as automotive, aerospace, and construction.
Extruders: Precise control of material flow and product dimensions is essential in extrusion processes, especially in the production of plastic, rubber, and metal products. Frequency converters offer the fine-tuned control needed to meet exacting standards for product quality.
2. Power Generation and Distribution
Frequency converters play a crucial role in the power generation sector, especially in the integration of renewable energy sources and maintaining consistent power quality in uninterruptible power supply (UPS) systems.
Renewable Energy Integration
The growing reliance on renewable energy sources such as wind and solar power has made frequency converters an essential technology for stabilizing and optimizing energy output:
Wind Power: Wind turbines generate electricity based on the varying speed of the wind. Frequency converters are used to adjust the output frequency of wind turbines, allowing seamless integration with the electrical grid. Without frequency converters, the fluctuating nature of wind energy could lead to instability and inefficiency in power supply.
Solar Power: Solar panels generate direct current (DC) electricity, which must be converted into alternating current (AC) and synchronized with the grid’s standard frequency. Frequency converters ensure that the energy produced by solar panels is delivered in a stable and efficient manner, preventing voltage spikes or frequency disruptions.
Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) Systems
In critical sectors such as healthcare, data centers, and telecommunications, where power interruptions can lead to disastrous consequences, frequency converters maintain consistent power quality:
Eliminating Voltage Sags and Surges: Frequency converters help regulate voltage levels, protecting sensitive equipment from power sags, surges, and interruptions. This is particularly important in environments where continuous operation is essential, such as hospitals and emergency services.
Maintaining Consistent Frequency: Many types of equipment, especially in industrial settings, rely on a specific operating frequency for optimal performance. Frequency converters ensure that this frequency remains consistent, minimizing the risk of equipment failure and maximizing efficiency.
3. Transportation
The transportation sector is rapidly evolving with the adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) and more energy-efficient railway systems. Frequency converters are integral to the operation and optimization of these technologies.
Electric Vehicles (EVs)
Frequency converters are a key component in electric vehicle powertrains, providing precise control over various vehicle functions:
Motor Speed and Torque: Frequency converters regulate the speed and torque of electric motors in EVs, enabling smooth acceleration, deceleration, and regenerative braking. This contributes to improved energy efficiency and a longer driving range, which are critical factors in the adoption of EVs.
Battery Charging: Frequency converters optimize the charging process by controlling the voltage and current delivered to the battery, reducing charging times and preventing overcharging. This is particularly important as fast-charging infrastructure becomes more widespread.
Railway Transportation
Electric trains and light rail systems rely on frequency converters for efficient and reliable operation:
Efficient Speed Control: Frequency converters enable the precise control of electric locomotives, ensuring smooth acceleration and deceleration. This is essential for maintaining passenger comfort, reducing energy consumption, and improving overall operational efficiency.
Regenerative Braking: When trains slow down, frequency converters capture the kinetic energy generated during braking and convert it back into electricity, which can be used to power other systems or fed back into the grid. This significantly improves the energy efficiency of railway networks.
4. Construction Industry
In the construction industry, frequency converters are used in various heavy machinery and systems to ensure safety and enhance operational efficiency.
Cranes and Hoists
The precise control of motor speed and torque provided by frequency converters is crucial for the safe operation of cranes and hoists:
Safety: Frequency converters minimize the risk of load swaying or uncontrolled movement by allowing operators to make fine adjustments to lifting speeds. This improves safety for workers and reduces the likelihood of accidents.
Operational Efficiency: With smoother load handling and more precise positioning, frequency converters increase the productivity of cranes and hoists, while also reducing wear and tear on the equipment.
HVAC Systems
In large commercial buildings and industrial facilities, heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems consume a significant amount of energy. Frequency converters optimize these systems by adjusting motor speeds to match the actual demand:
Fans and Pumps: By controlling the speed of fans and pumps, frequency converters reduce energy consumption and improve comfort levels in buildings. This not only leads to cost savings but also reduces the environmental impact of HVAC systems.
5. Oil and Gas Industry
In the oil and gas sector, precision and reliability are key. Frequency converters provide the control needed for efficient extraction, transportation, and processing.
Pump Control: In oil drilling and extraction operations, frequency converters precisely control the speed of pumps, ensuring consistent flow rates and reducing energy consumption. This is particularly important in offshore platforms, where energy efficiency is critical.
Compressor Optimization: In gas compression and processing plants, frequency converters optimize the speed of compressors, reducing energy consumption while maintaining consistent performance.
6. Marine Industry
Frequency converters are widely used in marine applications to control propulsion systems and optimize energy usage on ships and submarines.
Propulsion Motor Control: Frequency converters adjust the speed and torque of marine propulsion motors, allowing for smoother and more energy-efficient operation. This reduces fuel consumption and emissions, contributing to the overall sustainability of marine transportation.

Expanding Future Applications of Frequency Converters
As industries worldwide continue to prioritize energy efficiency, sustainability, and automation, the applications of frequency converters are expected to expand. Industries such as food and beverage production, chemical processing, and pharmaceuticals are increasingly adopting frequency converter technology to optimize their operations. Moreover, the push toward Industry 4.0 and smart manufacturing will likely lead to even more innovative uses for this transformative technology.
Conclusion
Frequency converter technology is revolutionizing industries by enabling the efficient, reliable, and safe operation of electrical equipment. From manufacturing and transportation to power generation and HVAC systems, frequency converters are essential for optimizing performance, reducing energy consumption, and ensuring sustainability. As technology continues to evolve and industries seek more efficient solutions, the role of frequency converters will only grow, contributing to advancements across a wide range of sectors.
By understanding the applications and advantages of frequency converters, businesses can make more informed decisions about integrating this technology into their operations, leading to increased productivity, reduced costs, and a more sustainable future.














 Contact Us
Contact Us


